Get Started
Deploy Axum with LaunchFlow
Deploy a Axum application to AWS Fargate with LaunchFlow.
View the source code for this guide in our examples repo.
0. Set up your Axum Project
If you already have a Axum Project you can skip to step #1.
Initialize your crate:
1cargo new launchflow-axum
2cd launchflow-axum
3cargo add axum
4cargo add tokio -F full
Update src/main.rs to have a simple handler:
1use axum::{routing::get, Router};
2
3#[tokio::main]
4async fn main() {
5 let lf_env = std::env::var("LAUNCHFLOW_ENVIRONMENT").expect("LaunchFlow environment not set");
6 let port = std::env::var("PORT").unwrap_or("3000".to_string());
7 let host = std::env::var("HOST").unwrap_or("0.0.0.0".to_string());
8 let address = format!("{host}:{port}");
9
10 let greeting = format!("Hello from {lf_env}!");
11 let app = Router::new().route("/", get(|| async { greeting }));
12
13 let listener = tokio::net::TcpListener::bind(address).await.unwrap();
14 axum::serve(listener, app).await.unwrap();
15}
Create a Dockerfile in the root directory of your create.
1FROM public.ecr.aws/docker/library/rust:1.71 as builder
2
3WORKDIR /app
4COPY . .
5
6RUN cargo build --release --bin launchflow-axum
7
8FROM public.ecr.aws/docker/library/debian:bullseye AS runtime
9
10WORKDIR /app
11COPY /app/target/release/launchflow-axum /usr/local/bin
12
13ENV HOST=0.0.0.0
14ENV PORT=80
15
16ENTRYPOINT ["/usr/local/bin/launchflow-axum"]
1. Initialize Launch Flow
Install the LaunchFlow Python SDK and CLI using pip.
1pip install launchflow[aws]
Initialize LaunchFlow in your project
1lf init --backend=local
- Name your project
- Select
Yesfor creating an exampleinfra.py - Select
AWSfor your cloud provider - Select
ECS Fargatefor your service
Once finished you will get an infra.py that looks like:
1import launchflow as lf
2
3# ECSFargateService Docs: https://docs.launchflow.com/reference/aws-services/ecs-fargate
4api = lf.aws.ECSFargateService(
5 "my-ecs-api",
6 dockerfile="Dockerfile", # Path to your Dockerfile
7)
ECSFargateService will build your Dockerfile and deploy to ECS Fargate. You can provide additional fields to ECSFargateService to configure things like machine type, num instances, or even a custom domain.
2. Deploy your Service
Make sure you have local AWS credentials set up before deploying.
1lf deploy
- Name your environment (
devis a good first name) - Select your cloud provider
AWS - Confirm the resources to be created
- Select the service to deploy
Once complete you will see a link to your deployed service on ECS Fargate.
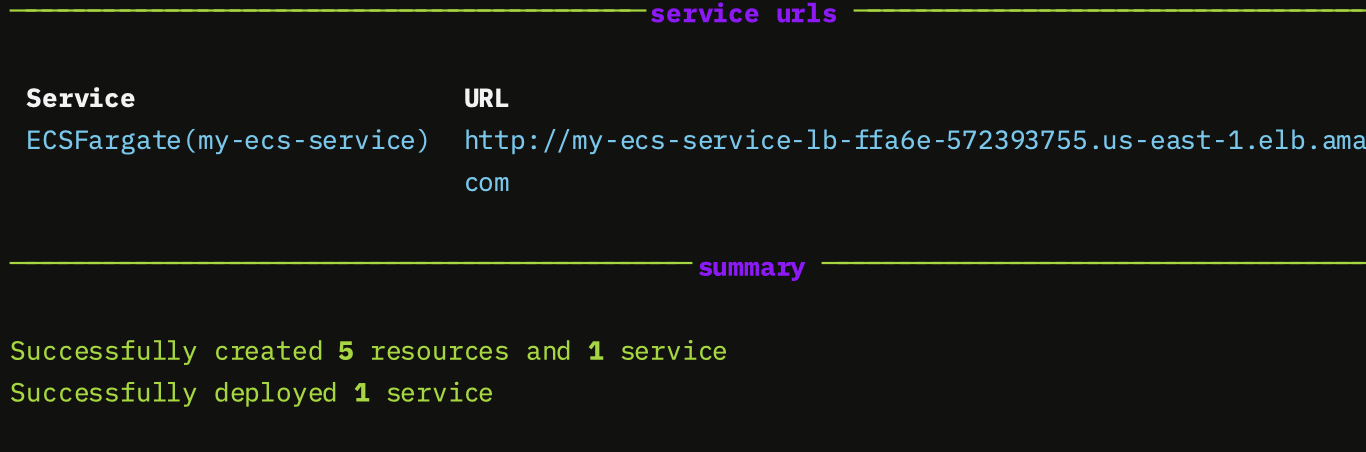
3. Cleanup your Resources
Optionally you can delete all your resources, service, and environments with:
1lf destroy
2lf environments delete
4. Visualize, Share, and Automate
LaunchFlow Cloud usage is optional and free for individuals.
Using the local backend like we did above works fine for starting a project, but doesn't offer a way to share state between multiple users. LaunchFlow Cloud is a web-based service for managing, sharing, and automating your infrastructure. It's free small teams and provides a simple, secure way to collaborate with your team and automate your release pipelines.
Sign up for LaunchFlow Cloud and connect your local environment by running:
1lf init --backend=lf
This will create a project in your LaunchFlow Cloud account and migrate your local state to the LaunchFlow Cloud backend.
What's next?
- Add resources to your application
- Promote your application to a production enviroment
- Learn more about Environments, Services, and Resources
- Join theLaunchFlow Slack community
- View your application in theLaunchFlow console

